Foam Copper: Properties, Applications, and Benefits
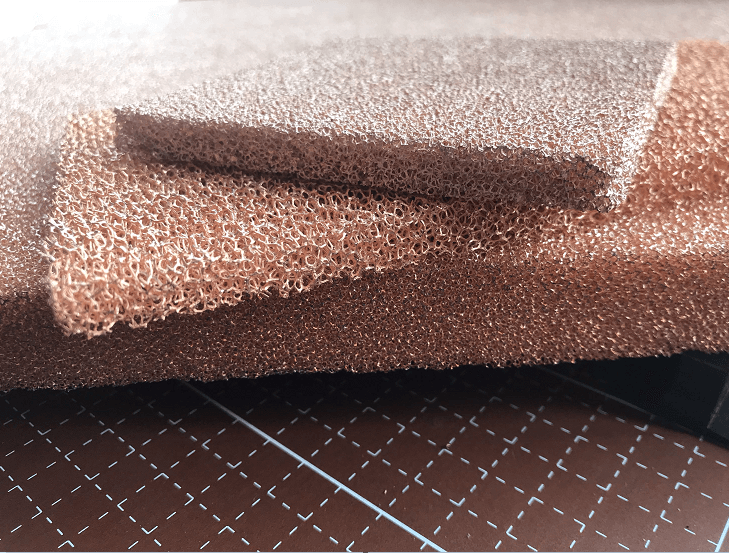
Foamed copper (also known ascopper foam) is a lightweight and porous material with a unique cellular structure that consists of interconnected copper pores. This material has gained increasing attention due to its combination of the excellent thermal and electrical conductivity of copper with the benefits of a porous structure, such as low weight and high surface area.
In this article, we will explore the properties of foamed copper, its manufacturing processes, and its wide range of applications across various industries.
●What is Foamed Copper?
Foamed copper is a type ofmetal foam that retains many of the characteristics of solid copper, such as its high electrical and thermal conductivity, while incorporating a porous, sponge-like structure. The material is lightweight, mechanically strong, and provides a large surface area-to-volume ratio, making it ideal for various high-performance applications.
Copper foam can be produced with varying porosities and cell sizes, depending on the desired application. It is available in different forms, such as sheets, blocks, or custom shapes, and can be used in both structural and functional roles.
●Properties of Foamed Copper
Foamed copper has several notable properties that make it highly valuable for a range of industrial and research applications:
1.High Electrical and Thermal Conductivity:
Copper is known for its excellent ability to conduct heat and electricity. Even in its foamed form, copper maintains a high level of conductivity, making it ideal for applications that require efficient heat dissipation or electrical conduction.
2.Lightweight:
The porous structure of copper foam drastically reduces its weight compared to solid copper, without sacrificing strength. This makes it useful for applications where minimizing weight is critical, such as in aerospace, automotive, and portable electronics.
3.Large Surface Area:
The open-cell structure of foamed copper provides a significantly larger surface area compared to a solid copper sheet of the same volume. This large surface area enhances the material's performance in applications such as heat exchangers, catalysis, and electrochemical processes.
4.Corrosion Resistance:
Like solid copper, copper foam is resistant to corrosion in various environments, including exposure to atmospheric conditions, water, and some chemicals. This makes it durable and suitable for long-term use in challenging environments.
5.Mechanical Strength:
Despite its lightweight nature, foamed copper exhibits good mechanical strength and structural integrity, allowing it to be used in load-bearing applications or as a support material.
6.Permeability:
The porous structure allows gases and liquids to pass through easily, making copper foam an excellent material for filtration, catalysis, and gas diffusion.
●Manufacturing Processes for Foamed Copper
There are several methods for producing foamed copper, each with its own advantages depending on the desired properties of the final product. The most common methods include:
1.Electroplating onto a Polymer Foam:
One common method is to coat a polymer foam template with a layer of copper throughelectroplating. After the desired thickness of copper has been deposited, the polymer template is removed, often by heating, leaving behind a porous copper structure. This technique allows for precise control over pore size and distribution.
2.Powder Metallurgy:
In the powder metallurgy process, copper powder is mixed with a foaming agent and compressed into a mold. The mixture is then heated, causing the foaming agent to release gas and create pores within the copper structure. This method allows for the production of copper foam with varying degrees of porosity.
3.Additive Manufacturing (3D Printing):
Advances inadditive manufacturing have made it possible to create complex copper foam structures with precisely engineered porosity. This method involves building the foam layer by layer using copper-based materials, allowing for the creation of custom shapes and optimized structures.
4.Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD):
In this method, copper is deposited onto a template using a vapor phase process. The template is then removed, leaving behind a porous copper structure. This process is particularly useful for creating foams with very fine pore structures.
●Applications of Foamed Copper
Due to its unique combination of properties, foamed copper is used in a variety of high-tech and industrial applications:
1.Heat Exchangers
Foamed copper's high thermal conductivity and large surface area make it an ideal material forheat exchangers and cooling systems. The open-cell structure allows for efficient heat transfer between the material and the surrounding medium, making it perfect for cooling electronic components, heat sinks, and radiators.
2.Energy Storage
Copper foam is used as a conductive substrate inbatteries andsupercapacitors. Its high surface area improves charge storage capacity and electrode performance. In particular, copper foam serves as a current collector fornickel-cadmium (NiCd) andlithium-ion batteries, enhancing the efficiency of the energy storage device.
3.Catalysis
In chemical reactions that require catalysts, foamed copper is used as a support material for the catalyst. The large surface area of the foam increases the number of active sites available for reactions, improving the efficiency of the process. Applications include fuel cells, hydrogen production, and gas purification systems.
4.Electrochemical Applications
The large surface area and high conductivity of foamed copper make it an excellent material forelectrochemical applications, such aselectrolysis andelectrodeposition. It is often used inelectrodes for various processes, including wastewater treatment and metal recovery.
5.Filtration
The porous structure of foamed copper allows it to be used as a filter for gases and liquids. It is particularly useful in environments where both high conductivity and filtration capabilities are required, such as inair filtration systems,chemical processing, andcatalytic converters.
6.Acoustic Damping
Foamed copper can be used forsound absorption andnoise reduction in industrial and automotive applications. Its cellular structure effectively absorbs sound waves, reducing noise levels in machinery and vehicle cabins.
7.Structural Applications
Due to its lightweight and mechanical strength, foamed copper can be used as alightweight structural material in industries such as aerospace and automotive. It is also used in composite materials, where it provides both strength and thermal management capabilities.
●Benefits of Using Foamed Copper
-High Efficiency in Thermal Management: Its ability to quickly dissipate heat makes copper foam invaluable in cooling systems for electronics, improving reliability and lifespan.
-Improved Energy Storage: Copper foam enhances the performance of energy storage devices, offering higher capacities and faster charge/discharge cycles.
-Sustainability: Copper is recyclable, and foamed copper can be reused or repurposed at the end of its life, contributing to sustainability efforts in various industries.
●Conclusion
Foamed copper combines the beneficial properties of copper—such as high electrical and thermal conductivity—with a porous, lightweight structure. This unique material has a wide range of applications in industries including electronics, energy storage, catalysis, and filtration. Its versatility, coupled with the ability to customize pore size and shape, makes foamed copper a critical material for advancing technology and industrial processes. As manufacturing techniques continue to evolve, we can expect foamed copper to play an even larger role in future innovations.